Electrophysiological brain activity refers to the electrical signals in the brain generated by neurons. We differentiate between:
-
Primary currents (direct result of neural activity)
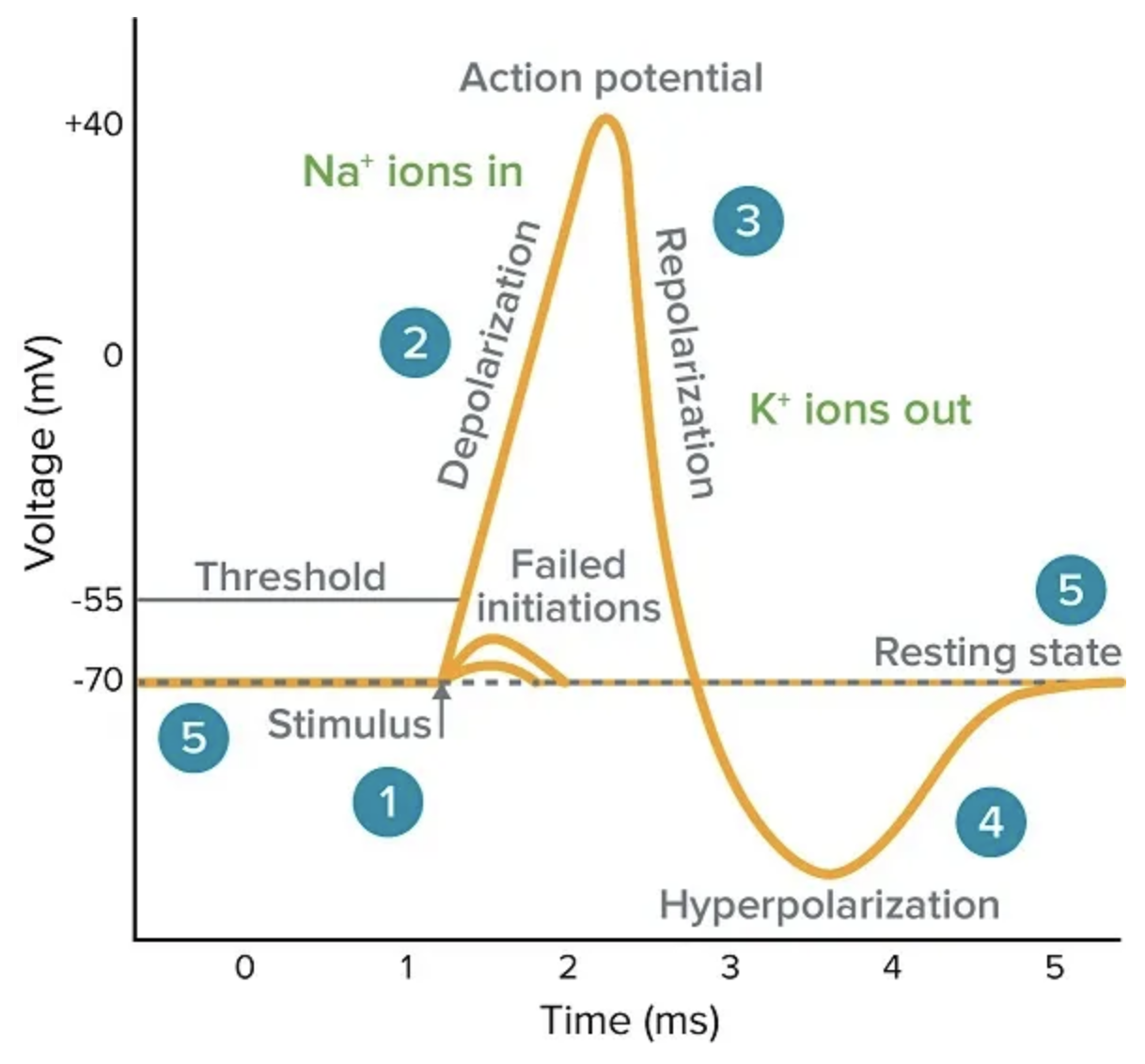
- Action potential currents
-
~1-2 ms duration
-
propagate along the axon of the neuron
-
caused by sodium and potassium ion flow across axonal membrane
-
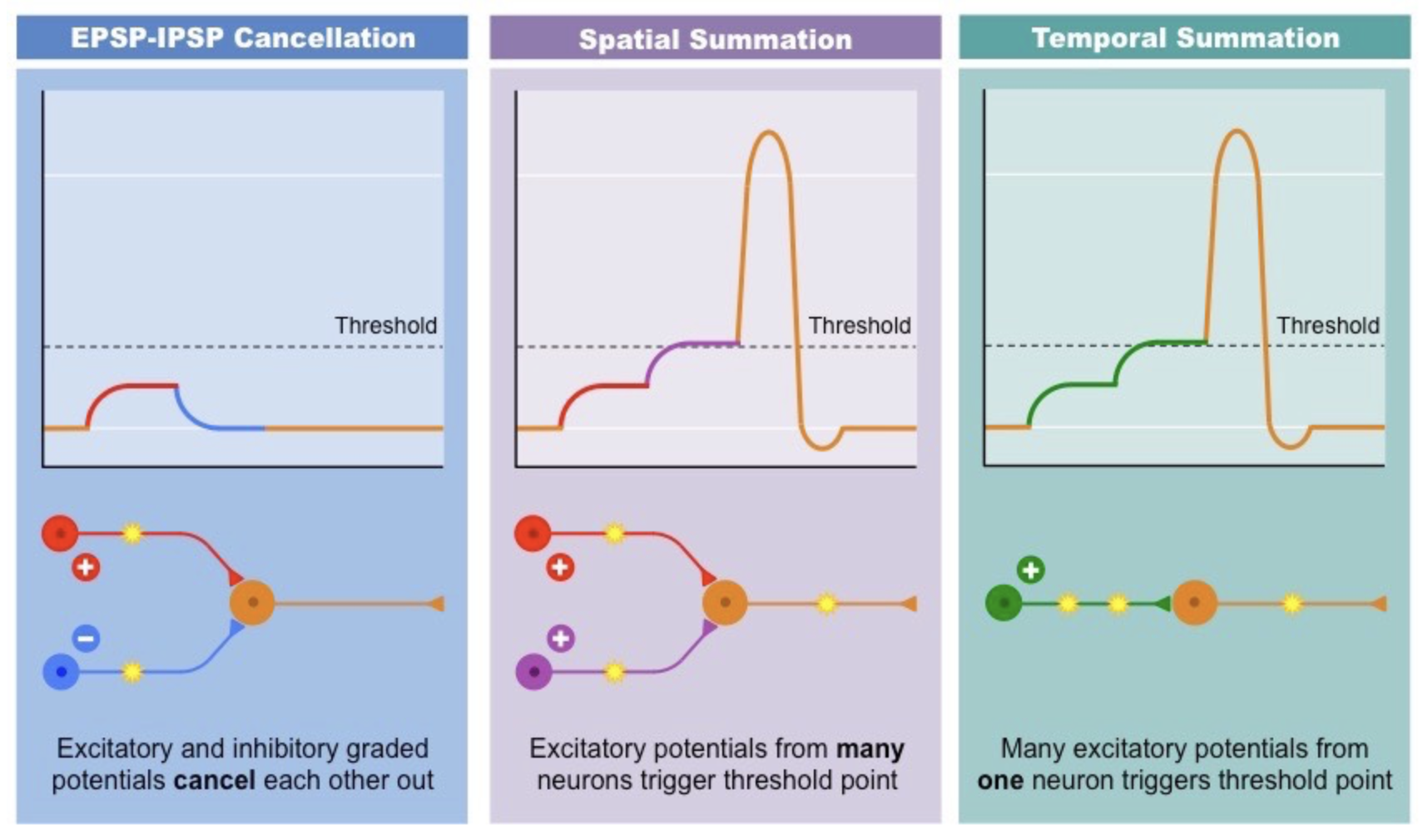
- Post-synaptic currents
-
10-100ms duration
-
occur at dendrites and soma when neurons receive synaptic input
-
caused by binding of neurotransmitters to receptors which creates ion flow
-
summation in space and time
-
- Action potential currents
-
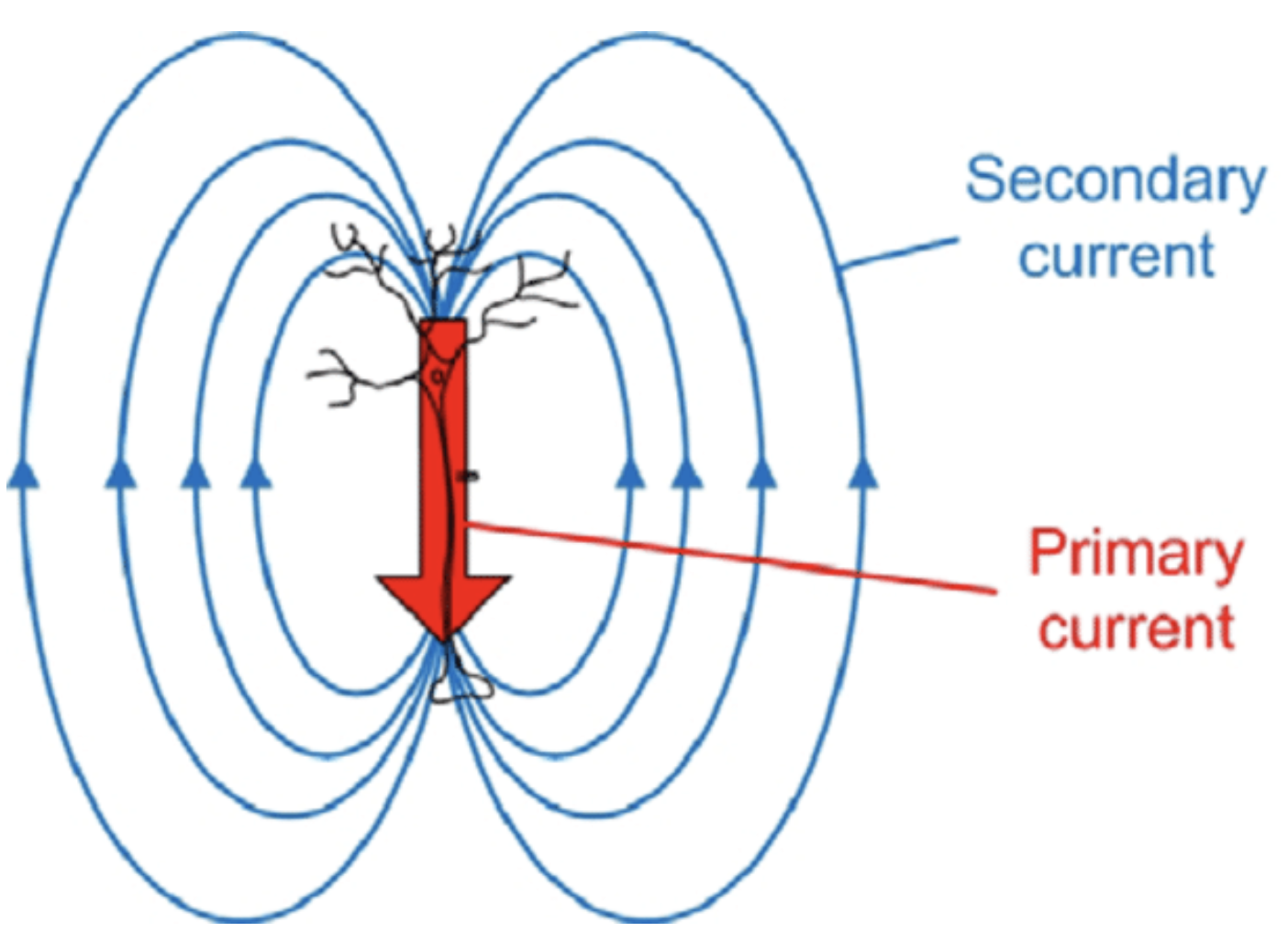
Secondary currents (induced by primary currents):
- Volume conduction currents
-
Brain is a conductive medium so electric potentials spread through tissues to surrounding neural structures (gray matter, white matter, CSF, skull, scalp)
-
- Volume conduction currents