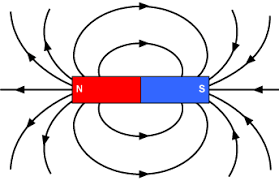
A magnetic field is a vector field that describes the influence of moving electric charges and time-varying electric fields on other charges and currents. It is governed by the Ampère-Maxwell’s law and Gauss’ law (magnetism) which states that magnetic field lines form closed loops, implying the absence of magnetic monopoles. The magnetic field exerts a force on a moving charge according to the Lorentz force law.