An electric field is a vector field that describes the force per unit charge exerted on a test charge due to the presence of other electric charges. An electric field can be generated by:
-
the presence of an electric charge (Gauss’ law)
-
a changing magnetic field (Faraday’s law)
-
moving charges or electromagnetic waves (Ampère-Maxwell’s law)
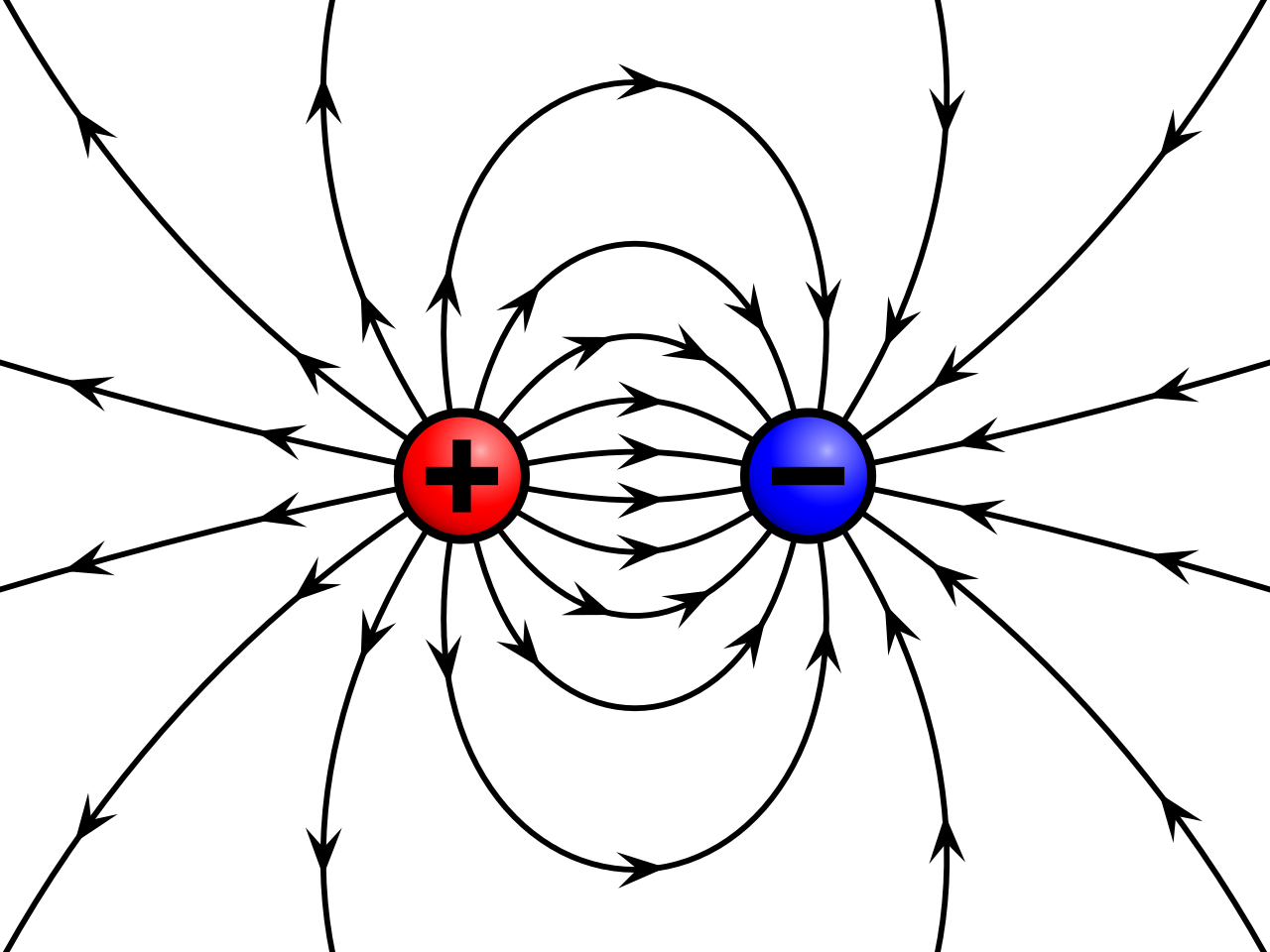
Mathematically, the electric field at a point is defined as:
| where | |
|---|---|
| electric field, measured in volts per meter | |
| position vector in three-dimensional space, typically expressed as and measured in meters | |
| time, measured in seconds | |
| electric test charge, measured in coulomb | |
| force vector experienced by the test charge, measured in newtons |